Physiotherapy plays crucial role in augmenting immunity and mental health during pandemic. It aids treatment and recovery of COVID-19 patients.
Physiotherapy’s role in non-COVID cases
Breathing exercises
1.DIAPHRAGMATIC BREATHING
2.PURSED LIP BREATHING
3.THORACIC EXPANSION EXERCISES
A) APICAL.
B)LATERAL COSTAL EXPANSION.
C)POSTERIOR BASAL EXPANSION.
4.BUTEYKO INSPIRED BREATHING.
5.SUSTAINED MAXIMAL INSPIRATION.
1.DIAPHRAGMATIC BREATHING
- Diaphragm is the main muscle which facilitates our breathing. Performing diaphragmatic breathing regularly is key to encouraging it
- Diaphragmatic breathing pattern concentrates on forward movement of the whole abdominal wall .
- Another technique combines forward movement of upper abdominal wall with some lateral movement of the lower ribs
- Place one hand over the anterior costal margins(CHEST)
- Other hand on upper abdomen to feel the movement occurring (breathe in gently and feel the air coming will around the waist)
- The upper abdomen will bulge forward slightly and the anterior margins will move up and out
- It is vital to remember that the expiratory phase is completely passive ;any forced or prolonged expiration may increase airways obstruction.
- Performing it 3-4 times at a stretch and 2-3 times a day will stimulate the diaphragm.
Position:
- Pursed Lip breathing technique is to sit comfortably on a chair with relaxed shoulders,
- Take in a deep breath from the nose and hold it and then exhale slowly via the mouth with pursed lips.
- This will create a small positive pressure which prevents the collapse of the airway.
3.Localised basal expansion
ADVANTAGES OF SEGMENTAL BREATHING:
Prevent accumulation of pleural fluid
5. The person may then be taught to perform the maneuver independently. by place the hand (s) over the ribs or apply resistance using a belt.
- Belt exercises reinforce lateral costal breathing (A) by applying resistance during inspiration and (B) by assisting with pressure along the rib cage during expiration.
- B. Right middle lobe or lingula expansion
- • Sitting Position.
- • Place your hands at either the right or the left side of the chest, just below the axilla.
- • Follow the same procedure as described for lateral basal expansion.
- c.Apical expansion
- • Sitting position.
- • Apply pressure (usually unilaterally) below the clavicle with the fingertips.
4.Buteyko breathing technique
5.SUSTAINED MAXIMAL INSPIRATION.
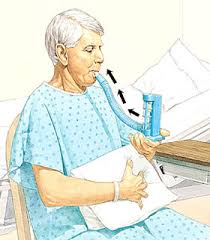
sustained maximal inspiration. A deep-breathing maneuver that mimics the normal physiological sigh mechanism. The patient inspires from a resting expiratory level up to maximum inspiratory capacity, with a pause at end inspiration.
An incentive spiro-meter is a medical device that facilitate SMI with incorporated visual indicators of performance (inspiratory effort) in order to aid the therapist in coaching the individual to optimal performance and likewise individual uses this visual feedback to monitor their own efforts. The device gives the individual visual feedback regarding flow and volume.
The visual dimension of the therapy serves as a motivation or goal for the patient to try to meet by repeating the maximal effort frequently.
Technique ;
- Person should be in a relaxed position suitable for deep breathing (e.g. sitting upright in a chair or side lying if extra volume is required in one lung due to ventilation perfusion matching).
- Person creates a tight seal around the mouthpiece and inhales deeply and slowly. Than watches the flow meter for visual feedback. If possible the we can sustains the inhalation to create an end-inspiratory hold. Ideally, the inhalation is sustained for 4-5 seconds.
- Than relaxes seal around the mouthpiece and exhales; normal breathing is resumed with relaxed shoulder girdle.
- However, using an incentive device as feedback may create greater inhaled volumes, greater control of flow and more motivation to participate in therapy.